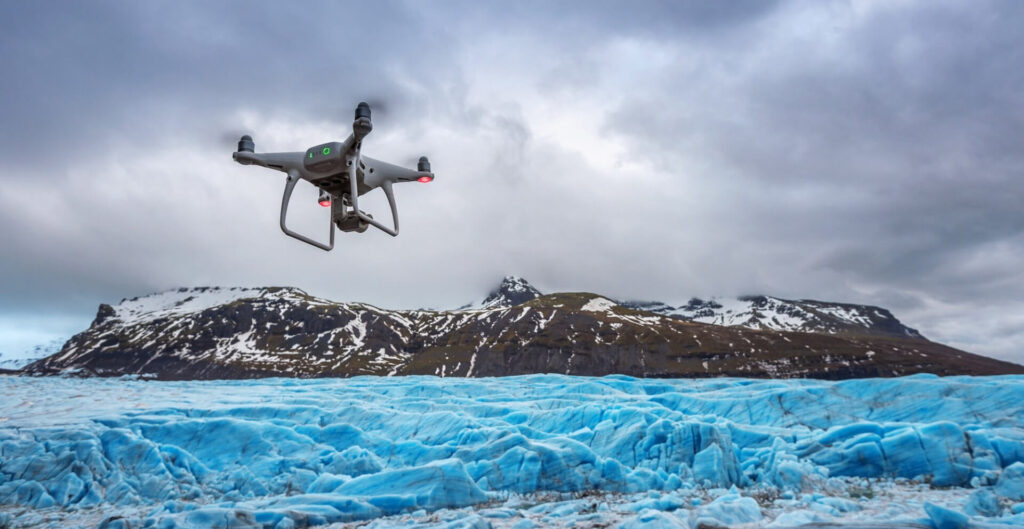
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are playing an increasingly crucial role in environmental conservation. Their ability to access hard-to-reach areas, collect high-resolution data, and monitor vast landscapes in real-time makes them invaluable tools for conservationists. Here’s an in-depth look at how drones are enhancing environmental conservation efforts across the globe.
1. Wildlife Monitoring and Protection
Tracking Animal Populations: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal sensors are used to monitor wildlife populations, track migrations, and observe behavior patterns. This non-invasive method allows researchers to gather accurate data without disturbing the animals.
Anti-Poaching Efforts: Drones patrol wildlife reserves and protected areas, detecting illegal activities such as poaching. Equipped with night vision and thermal imaging, drones can operate day and night, providing real-time alerts to rangers and law enforcement, thus enhancing the protection of endangered species.
Habitat Mapping: Drones create detailed maps of wildlife habitats, identifying changes in vegetation, water sources, and other critical factors. This information helps in understanding the needs of different species and planning effective conservation strategies.
2. Forest and Land Management
Deforestation Monitoring: Drones provide frequent and accurate data on forest cover, detecting illegal logging and deforestation activities. This timely information enables authorities to take immediate action to protect forests.
Reforestation Projects: Drones are being used in innovative reforestation projects, where they drop seed pods into deforested areas. This method is faster and more efficient than traditional tree-planting techniques, helping to restore degraded ecosystems quickly.
Soil and Erosion Analysis: By capturing detailed topographical data, drones help in assessing soil health and erosion patterns. This information is vital for implementing soil conservation practices and preventing land degradation.
3. Marine and Coastal Conservation
Monitoring Marine Life: Drones are used to monitor marine ecosystems, tracking the health of coral reefs, fish populations, and marine mammals. Aerial surveys provide comprehensive data that is difficult to obtain through underwater methods alone.
Coastal Erosion Studies: Drones map coastal areas, providing data on shoreline changes and erosion rates. This information is crucial for developing strategies to protect coastal environments and communities from the impacts of climate change.
Pollution Detection: Drones equipped with specialized sensors can detect oil spills, plastic pollution, and other contaminants in water bodies. Early detection allows for swift remediation efforts to minimize environmental damage.
4. Climate Change Research
Glacial Monitoring: Drones are used to monitor glaciers and ice caps, capturing data on their size, movement, and melt rates. This information contributes to understanding the impacts of climate change on polar and mountainous regions.
Vegetation and Phenology Studies: Drones collect data on vegetation health, phenology (the study of cyclic and seasonal natural phenomena), and carbon sequestration. This helps researchers track changes in plant growth patterns and their implications for carbon storage and climate regulation.
Weather and Atmospheric Research: Drones are deployed to study weather patterns, atmospheric conditions, and greenhouse gas emissions. This data is critical for climate modeling and developing strategies to mitigate climate change.
5. Disaster Response and Environmental Protection
Natural Disaster Monitoring: Drones provide real-time data during natural disasters such as wildfires, floods, and hurricanes. They help assess the extent of damage, monitor ongoing threats, and coordinate response efforts, reducing the environmental impact of such events.
Post-Disaster Recovery: After a disaster, drones assess the environmental damage and guide recovery efforts. They help identify areas that need reforestation, soil stabilization, and other restoration activities to restore the ecosystem.
6. Advancements and Future Prospects
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning with drone technology enhances data analysis capabilities. AI-powered drones can autonomously identify species, track changes, and predict environmental trends, making conservation efforts more efficient and effective.
Collaborative Efforts: Increased collaboration between governments, NGOs, and private sectors will drive the development and deployment of drones in conservation. Shared data and resources will enhance the global impact of these efforts.
Regulatory Support: Developing supportive regulatory frameworks for the use of drones in conservation will ensure their safe and ethical deployment. Clear guidelines will help balance the benefits of drone technology with concerns about privacy and wildlife disturbance.