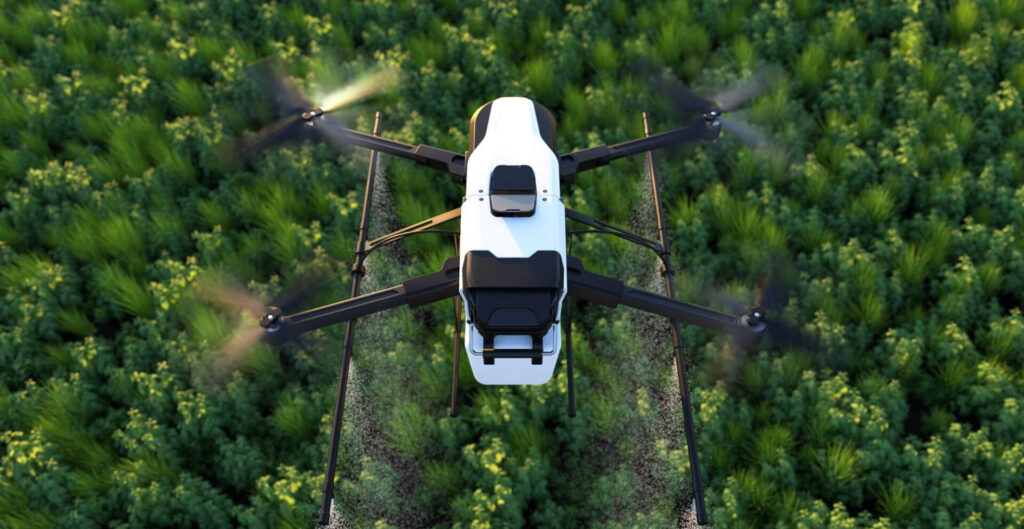
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are revolutionizing various industries by providing innovative solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and open new revenue streams. However, integrating drones into commercial and public operations also presents significant challenges. Here, we explore the economic benefits and challenges associated with drone integration.
Economic Benefits of Drone Integration
1. Cost Savings
Reduced Labor Costs: Drones automate tasks that traditionally require significant human labor, such as inspections, surveying, and monitoring. This automation reduces the need for manual labor, leading to substantial cost savings for businesses.
Lower Operational Costs: Drones offer a more affordable alternative to traditional methods such as manned aircraft for aerial surveys and inspections. Their lower operational costs make them an economically viable option for many industries.
Efficient Resource Management: In agriculture, drones enable precision farming techniques, allowing for targeted application of fertilizers, pesticides, and water. This precise management reduces resource wastage and increases crop yields, leading to cost savings and higher profitability.
2. Increased Productivity
Rapid Data Collection: Drones can quickly gather data over large areas, significantly reducing the time required for tasks like land surveying, infrastructure inspections, and environmental monitoring. This rapid data collection enhances productivity and accelerates project timelines.
Improved Accuracy: High-resolution imaging and advanced sensors enable drones to capture precise data, improving the accuracy of tasks such as mapping, monitoring, and inventory management. This accuracy reduces errors and rework, further enhancing productivity.
3. Enhanced Capabilities
Access to Hard-to-Reach Areas: Drones can access areas that are difficult or dangerous for humans to reach, such as disaster zones, tall structures, and remote locations. This capability expands the scope of operations and opens up new opportunities for businesses.
Real-Time Insights: Equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, drones provide real-time data and insights. This real-time information enables businesses to make informed decisions quickly, improving responsiveness and efficiency.
4. New Revenue Streams
Aerial Photography and Videography: Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography, creating opportunities in industries such as real estate, tourism, film, and advertising. Businesses can generate new revenue streams by offering drone-based services.
Delivery Services: The potential for drone delivery services in sectors like e-commerce, healthcare, and logistics promises new business models and revenue opportunities. Companies can leverage drones for faster and more efficient delivery solutions.
Economic Challenges of Drone Integration
1. Regulatory Hurdles
Compliance Costs: Navigating complex regulatory environments can be costly and time-consuming. Businesses must invest in understanding and complying with regulations related to drone operations, including registration, pilot certification, and operational limits.
Evolving Regulations: As drone technology evolves, regulations are continually updated. Keeping up with changing rules and ensuring compliance can be challenging and require ongoing investment in regulatory knowledge and resources.
2. Safety and Liability Concerns
Accidents and Incidents: The risk of accidents and incidents involving drones poses safety concerns. Businesses must implement rigorous safety protocols and invest in training to mitigate these risks, which can increase operational costs.
Insurance and Liability: Obtaining insurance coverage for drone operations can be expensive. Businesses need to protect themselves against potential liabilities arising from drone-related accidents, property damage, or privacy breaches.
3. Technological Limitations
Battery Life and Range: Current drone technology is limited by battery life and range, restricting the duration and distance of drone operations. This limitation can affect the feasibility and efficiency of certain applications.
Payload Capacity: The payload capacity of drones is limited, which can constrain their ability to carry heavy or bulky items. This limitation impacts the use of drones in industries such as delivery and construction.
4. Public Perception and Privacy Issues
Privacy Concerns: Drones can raise privacy concerns among the public, particularly when used in populated areas. Businesses must navigate these concerns by adhering to privacy laws and ensuring transparent and ethical use of drone technology.
Public Acceptance: Gaining public acceptance for drone operations can be challenging. Negative perceptions and concerns about safety, noise, and privacy can hinder the widespread adoption of drones.
5. Investment and Maintenance
Initial Investment: The initial investment in drone technology, including hardware, software, and training, can be significant. Small businesses and startups may find these costs prohibitive, limiting their ability to integrate drones into their operations.
Ongoing Maintenance: Maintaining and updating drone equipment and software is essential for safe and efficient operations. These ongoing maintenance costs can add to the overall expenses of using drones.